Lighting technologies
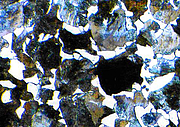
Lighting technologies using the example of normalized C45 steel (Nital etching)
Bright field
- lighting technology: bright field
- optical path: almost vertical
- application: approx. 50 % of all metallographic examinations
- optical features, accessories: none
- characterization: ferrite (bright), pearlite (dark), grain and phase boundaries (dark)
- comment: none
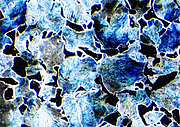
Dark field
- lighting technology: dark field
- optical path: angular illumination
- application: surface boundary contrast (scratches, cracks and pores), elevations and depressions (bright), planar surfaces (dark)
- optical features, accessories: none
- characterization: ferrite (dark), pearlite (bright), grain and phase boundaries (bright)
- comment: translucent phases
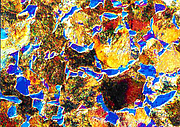
Polarization
- lighting technology: polarization
- optical path: corresponds to bright field, in addition necessary: polarizer, analyzer, compensation plate (optionally)
- application: analysis of all non-cubic phases
- optical features, accessories: polarizer, analyzer, compensation plate
- characterization: ferrite (dark), pearlite (bright)
- comment: application of zinc, titanium, magnesium and their alloys; color etching; non-cubic slag inclusions
Nomarski interference contrast
- lighting technology: Nomarski interference contrast
- optical path: almost vertical, in addition necessary: Nomarski prism slider (Wollaston prism), polarizer, analyzer, compensation plate (optionally)
- application: examination of slight roughnesses and differences in height (above some 10 nm), color and stereophonic imaging
- optical features: Nomarski prism slider, compensator, analyzer, compensation plates
- characterization: ferrite (blue), pearlite (yellow-brown-red)
- comment: none